Inland Pro Micro Starter Kit

Contents
1. Description
2. Component List
3. Installing Arduino IDE And Driver
4. Specification
5. Projects
- Hello World!
- LED Blinking
- Advertising Lights
- Button Controlling LED
- RGB LED
- Photosensitive LED
6. Resources
1. Description
Containing resistors with different resistance values, different colors LEDs, buttons, IR receiving components, this kit is compatible with various microcontrollers and Raspberry Pi.
Included in this kit, the Micro control board belongs to the Arduino series microcontroller and is compatible with the Arduino development platform.
To make you have a better understanding with these components and Micro control board, we will also provide some learning courses based on the Arduino, like wiring methods, test code, etc.
2. Component List
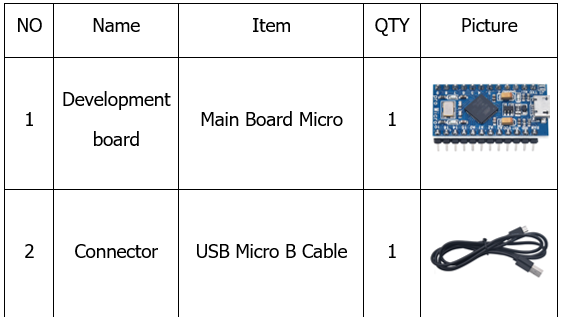



3. Installing Arduino IDE And Driver
When we get the development board, we firstly need to install the Arduino IDE and driver. The related files can be found on the official website. The following links you could refer to:
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/OldSoftwareReleases#1.5.x
Next to introduce installation method of Arduino-1.5.6 version IDEfor Windows system.
Download arduino-1.5.6-r2-windows.zip compressed folder and unzip it.
Double click Arduino-1.5.6 .exe file

Next step

Next step

Complete driver installation, click “Close” as shown below


Next to install Micro control board. This control board uses ATmega32u4 main chip and comes with USB to serial port function.
For Windows 10 system, the computer will automatically install the driver after connecting the Micro control board to the computer with a micro USB cable.
Click Computer--Properties--Device Manager, as shown below.
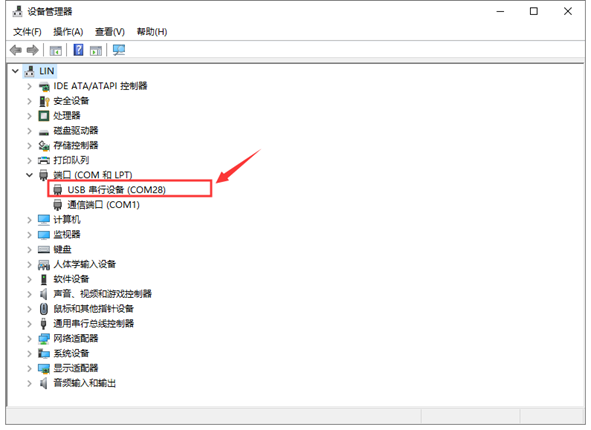
For other systems (Windows system), after connecting to the computer, the unknown device is displayed in the device manager. We can refer to the method of changing the driver on the computer ( Windows system) and reinstalling the driver.
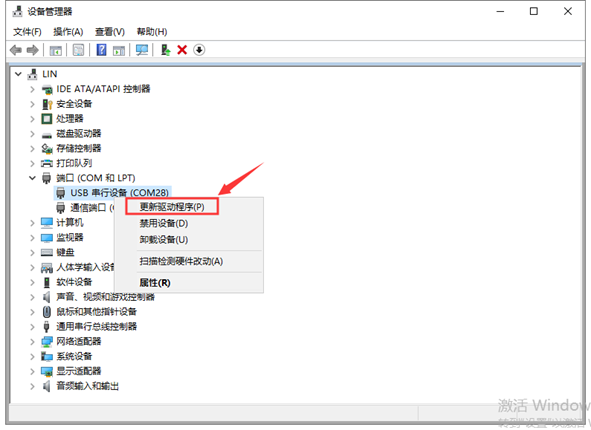
Enter the following page.

Find Arduino IDE installing address and drivers file, such as my defined driver address:
C:\Program Files (x86)\Arduino\drivers

Click “Next Step” to start installing.
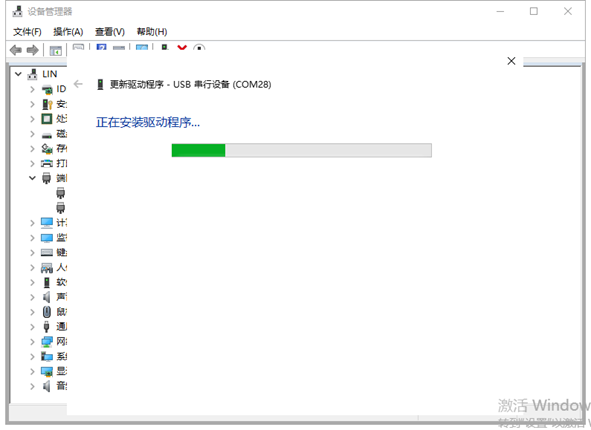
Finish installing, click to “close”

The driver is now installed. Click Computer-Properties-Device Manager, as shown below:
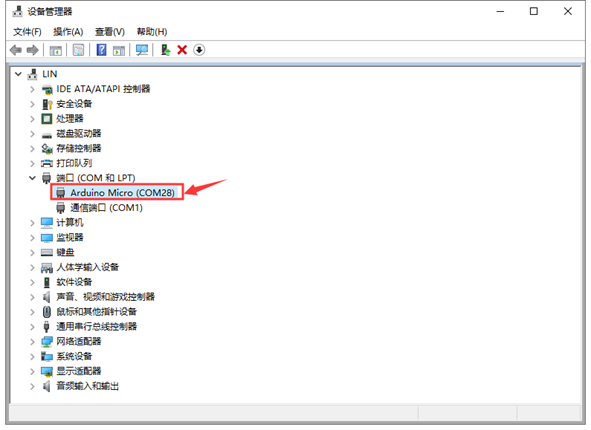
4. Specification
Micro Control Board:
Digital port:RX(D0)、TX(D1)、D2-D10、D14-D16、A0-A3(D18-D21)
Digital port:A0-A3、D4(A6)、D6(A7)、D8(A8)、D9(A9)、D10(A10)
PWM port (Pulse width modulation):D3、D5、D6、D9、D10
External Interrupt interface:D3 (interrupt 0), D2 (interrupt 1), D0 (interrupt 2), D1 (interrupt 3), and D7 (interrupt 4)
Serial communication interface:RX(D0)、TX(D1)
SPI communication interface:D14(MISO)、D15(SCLK)、D16(MOSI)
I2C communication interface:D2(SDA)and D3(SCL)
RAW: external power supply DC 7-9V
5. Projects
Hello World!
Description
After installing USB driver of Micro control board, we can find the corresponding serial port in Windows Device Manager. The burning of the first program is shown below. The serial monitor shows "Hello world!".
Equipment
- Micro control board*1
- USB cable*1
Wiring Diagram

Test Code
int val;
int ledpin=13;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(ledpin,OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
val=Serial.read();
if(val=='R')
{
digitalWrite(ledpin,HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(ledpin,LOW);
delay(500);
Serial.println("Hello World!");
}
}
Test Result
Open Arduino software, set board as shown below.

Set COM port, as shown below.

Click Verify to compile the program, check if the program is right; click
Upload to upload program; after setting up Micro control board, as shown below:

Upload successfully, enter “R”, click to “send”, serial monitor displays “ Hello World!”

Congratulation! Upload successfully!
LED Blinking
Description
The blinking LED experiment is quite simple. In this experiment, we’ll complete experiment using other digital I/O ports and external light.
Equipment
- Micro control board*1
- USB cable*1
- LED*1
- 220Ω Resistor*1
- Breadboard*1
- Male to female Dupont Lines
Wiring Diagram

Test Code
int led = 2; //Define digital port 2
void setup()
{
pinMode(led, OUTPUT); //Set led to output}
void loop()
{
digitalWrite(led, HIGH); //Turn on led
delay(1000); //delay for 1000ms
digitalWrite(led, LOW); //Turn off led
delay(1000);//delay for 1000ms
}
Test Result
After downloading program, you will see the LED connected to IO port blinking, with an interval approximately one second. The blinking LED experiment is now completed.
Advertising Lights
Description
In life, we often see some billboards composed of colorful led lights. Different effects shown on billboard as lights change. In this section, we simulate the effect of advertising lights with LED lights.
Equipment
- Micro control board*1
- USB cable*1
- LED*5
- 220Ω Resistor*5
- Breadboard*1
- Male to female Dupont Lines
- Male to male Dupont Lines
Wiring Diagram

Test Code
int BASE = 2 ; //the first LED is connected to I/O port
int NUM = 5; //the sum of LED
void setup()
{
for (int i = BASE; i < BASE + NUM; i ++)
{
pinMode(i, OUTPUT); //set I/O port to output }
}
void loop()
{
for (int i = BASE; i < BASE + NUM; i ++)
{
digitalWrite(i, HIGH); //set I/O to “HIGH”, light is on delay(200); //delay
}
for (int i = BASE; i < BASE + NUM; i ++)
{
digitalWrite(i, LOW); //set I/O to “LOW”", light is off delay(200); //delay
}
}
Test Result
After downloading the program, the external small light gradually brightens then darkens, and alternates.
Button Controlling LED
Description
I/O port means interface for INPUT and OUTPUT. Up until now, we’ve only used the output function.
In this experiment, we will try to use the input function, which is to read the output value of device. We’ll complete an experiment with use 1 button and 1 LED to give you a better understanding of the I/O function.
Equipment
- Micro control board*1
- USB cable*1
- LED*1
- Button *1
- 220Ω Resistor*1
- 10KΩ Resistor*1
- Breadboard*1
- Male to female Dupont Lines
- Male to male Dupont Lines
Wiring Diagram

Test Code
int ledPin = 7; //define digital port 7
int inputPin = 2; //define digital port 2
void setup()
{
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); //set ledPinto to output
pinMode(inputPin, INPUT); //set inputPin to input
}
void loop()
{
int val = digitalRead(inputPin);
//set digital variable val,read the value of digital port 2,assign the value for val
if (val == LOW) //when val is low level,LED gets dark
{
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // LED gets dark
}
else
{
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // LED gets bright
}
}
Test Result
After downloading the program and powering on, the LED light is on when the button is pressed, otherwise it is off.
RGB LED
Description
RGB lights can adjust the intensity of three primary colors (red / blue / green) through the PWM voltage input of the three pins R, G, and B to achieve the full-color mixing effect.
In this experiment, we control the RGB lights to display different colors by controlling the PWM values of the three PWM ports. The description of the RGB light interfaces are shown below.

Equipment
- Micro control board*1
- USB cable*1
- RGB LED*1
- 220Ω Resistor*3
- Breadboard*1
- Dupont Lines
- Breadboard cables
Wiring Diagram

Test Code
int redpin = 9 //select the pin for the red LED
int greenpin =6;// select the pin for the green LED
int bluepin =5; // select the pin for the blue LED
int val;
void setup() {
pinMode(redpin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluepin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenpin, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop()
{
for(val=255; val>0; val--)
{
analogWrite(9, val);
analogWrite(6, 255-val);
analogWrite(5, 128-val);
delay(1);
}
for(val=0; val<255; val++)
{
analogWrite(9, val);
analogWrite(6, 255-val);
analogWrite(5, 128-val);
delay(1);
}
Serial.println(val, DEC);
}
Test Result
After downloading the program and powering on, the external RGB light displays various colors alternately.
Photosensitive LED
Description
Since the photo resistor is an element that can change the resistance value according to the light intensity, the analog value needs to be read via analog port.
In this experiment, we design a circuit that reading different analog value and mapping analog value into PWM value under different light intensities, which controls the brightness of LED. Therefore, we achieve different brightness change of led as light intensity changes.
Equipment
- USB cable*1
- Micro control board*1
- LED*1
- Photo resistor*1
- 220Ω Resistor*1
- 10KΩ Resistor*1
- Breadboard*1
- Male to female Dupont Lines
- Male to male Dupont Lines
Wiring Diagram

Test Code
int ledpin=6;//define digital port 6 (PWM outputs)
void setup()
{
pinMode(ledpin,OUTPUT);//set digital port 6 to output
Serial.begin(9600);//set baud rate to 9600
}
void loop()
{
int val=analogRead(0);//read value of analog port A0
Serial.println(val);//display val variable
val = map(val, 0, 1023, 0, 255);//map form 0-1023 to 0-255
analogWrite(ledpin,255-val);// turn on LED and set the brightness
delay(10);//delay for 0.01s
}
Test Result
After downloading the program, the photo resistor senses that the brighter the light, the darker the LED; it senses that the darker the light, the brighter the LED. Open the serial port monitor, set baud rate to 9600, and you can see the analog value of photo resistor that senses the external light intensity.