Looking to upgrade or add RAM to your desktop or laptop computer? This article will help you to address some of the most common questions of how to select the correct RAM for your computer.
Q: What Is RAM?
A: The acronym RAM references Random Access Memory, and it is used for temporary storage by the CPU and GPU in computer functions. Some characteristics of RAM include:
- RAM is continuously overwritten and refreshed.
- RAM is much faster than any long-term storage device.
- RAM can only hold data while powered.
Q: What is the difference between desktop RAM and laptop RAM?
A: Desktops use DIMM, an acronym for Dual In-Line Memory Module.

A: Laptops use SO-DIMM, an acronym for Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module.

Q: What are the different types of RAM?
A: There are several different types of RAM. Most commonly, RAM is referred to as one of these types:
Most, if not all, modern PCs today use DDR4 RAM. When upgrading, make sure to determine what type of RAM you currently have installed. DDR3 is not forward compatible with DDR4 devices. DDR4 is not backward compatible with DDR3 motherboards. Very few motherboards may have compatible slots for both DDR4 and DDR3. They are not compatible to run together on the same system. DDR5 is also not backwards compatible.
Q: Which Type of RAM Do I Need?
A: To determine what RAM is compatible with your existing system, you can follow these steps:
From the Windows Start menu, search for System Information on your computer and open the app.
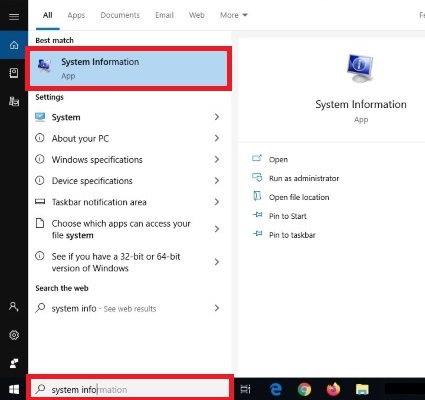
Under System Summary, you will find your Processor.

Using this information, search for your specific processor on the manufacturer's website to see what RAM is compatible with your processor. Motherboards also have compatibility requirements; however, they align directly with the corresponding requirements of compatible processors.
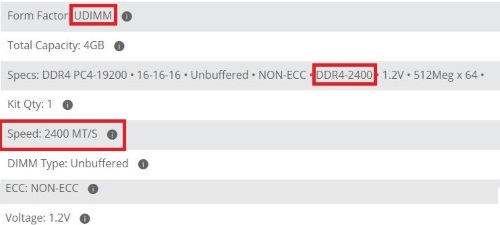
Q: What Speed of RAM do I need to purchase?
A: Several factors come together to determine the best answer:
- CPU and Motherboards have limitations, but most modern CPUs can support from 64GB up to 128GB of RAM. If you have concerns about the limits of your CPU or motherboard, search the model number's specific compatibility requirements on the corresponding manufacturer’s website.
- The clock speed of RAM is measured in MHz.
- The faster your RAM speed, the faster the system will function. For example, if you are gaming, 3000MHz is a great middle-ground to shoot for.
- Other programs will perform better with faster RAM. Determine what the purpose of your system is, then select your speeds while considering that information. In most modern PCs, it is possible to overclock your RAM. Additionally, most RAM available today is also backward compatible to a certain point, meaning if your RAM is capable of faster speeds than your CPU or motherboard was designed for, then the RAM will drop back to the highest compatible speed - within reasonable limitations.
Q: What Is the Difference Between Single RAM and Dual Channel RAM?
A: There are several differences to be aware of: Single channel is using one module of RAM, Dual channel uses two modules of RAM, and Quad-channel would be four modules of RAM. (Not all CPU and Motherboard combinations support quad-channel memory, so be sure to check your specifications prior to making this decision). When it comes to gaming, Single channel can be a fine starting point. However, when applying your PC to professional jobs that need to transfer more data constantly, then Dual or Quad channel will be the better option. Like a roadway, using one lane at rush hour causes traffic to back up - the same goes for RAM. For example, if you are using one large capacity module (16GB x 1), you can only transfer so much data between the CPU and RAM at one time. However, if you were to have two lower capacity modules (8GB x 2), you are effectively doubling the amount of information that can be processed at one time because you have twice as many lanes to choose from, allowing you to complete more processes using the same amount of RAM - 16GB. To prevent the likelihood of bottlenecking, Dual or Quad channel RAM options would be the better choice.
Q: What about RAM Timings and Latency?
A: CAS / CL or Column Access Strobe latency is the amount of time that needs to pass from the read command being issued to the data being available for the processor to access. DDR4 latency is measured in clock cycles rather than nanoseconds. The lower the latency, the faster your RAM can move on to the next process. Each RAM module has a rating for timings. Timing is expressed as a series of four numbers, like 5-5-5-15. This is how latency is measured. A high clock speed with higher frequency is better than low clock speed and low frequency.

Q: Should I focus on low latency or high clock speed for my RAM?
A: The speed rating of your RAM module is an expression of its data transfer rate. Latency is how fast a RAM module can access its own hardware. Lower numbers result in faster data access. The faster the RAM can access data, the faster that data is transferred to your CPU. Having more RAM available, or think of it as higher capacity, with a fast clock speed is recommended over less RAM or lower capacity and lower latency.
Remember, RAM is typically the easiest component to upgrade in your system. If you are building a budget PC go for higher capacity first if you have to choose. It is better to have two modules than one. Depending on the task, more RAM may not be needed. For gaming, you will be fine with 8GB. For other more intensive programs that need to transfer a lot of data, 16GB or more can result in faster performance.